A lung biopsy is a diagnostic procedure where we take a small piece of the lung tissue for a detailed analysis in the laboratory. In this article we discuss about. The indications of lung biopsy in children, how the procedure is performed and what can be the associated complications.
What are the conditions where a lung biopsy might be required in a child?
Lung biopsy in children is recommended in cases of diffuse lung diseases or interstitial lung diseases. Interstitial lung diseases or diffuse lung diseases is a large group of disorders which present with similar signs and symptoms. Interstitial lung diseases in children could be pulmonary hemosiderosis, non specific interstitial pneumonitis, eosinophilic lung diseases, chronic interstitial pneumonia and hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Lung biopsy is usually considered in children with interstitial lung diseases when the CT scan picture, blood tests and other findings are not conclusive. Lung biopsy in such situations provides very useful information needed to confirm the diagnosis and guide treatment.
Sometimes children might be having infection in their lungs and the diagnosis cannot be made by other investigations, including the bronchoscopy and bronchoalveolar lavage. In such a situation, the lung biopsy might be required for diagnosis. Such situations usually arrive in children who are immune-compromised, such as children on cancer treatment and bone marrow transplant patients.
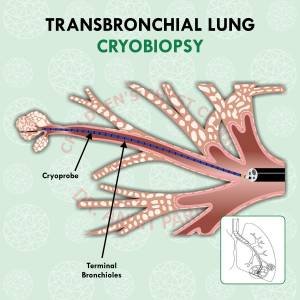
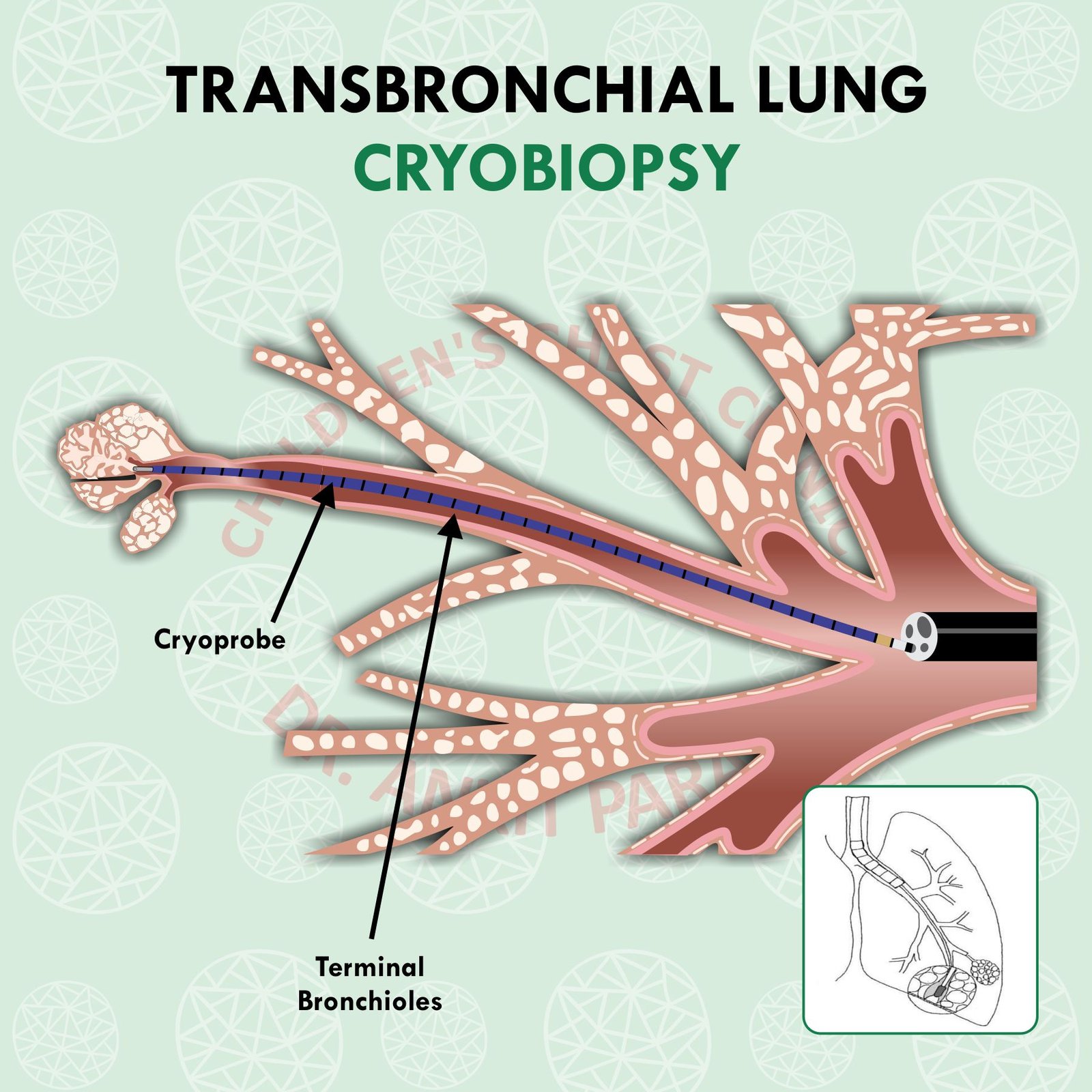
How is a lung biopsy performed?
Lung biopsy can be attained in many ways. The most common way by which a long biopsy is obtained is through a bronchoscope. A flexible bronchoscopy is performed and through the channel of the flexible bronchoscope a small forceps is passed which is then visualised with a dynamic X ray, known as the fluoroscopy. The forceps is used to take 3-5 small lung biopsy specimens. Recently instead of using a forceps, a cryoprobe is used to take a lung biopsy sample. The sample obtained by a cryoprobe is larger in size as compared to a forceps biopsy and hence provides better results. Flexible bronchoscopy guided lung biopsy is usually performed in the bronchoscopy suite under sedation and anesthesia.
Lung biopsy can also be attained by passing a needle from the chest under ultrasound or CT guidance. Surgical lung biopsy is also a method where the surgeon takes a long biopsy using a thoracoscope. This procedure is performed under general anesthesia and provides a large tissue for examination.
What tests are done on the lung biopsy which is performed?
Specimens of the lung biopsy are subjected to detailed histopathological analysis and cultures. Many specific stains and markers are now available to make a confirmed diagnosis which is required in many conditions.
What risks are associated with this procedure?
The risks associated with the procedure of lung biopsy includes bleeding into the lungs and collapse of the lung leading to air inside the pleural cavity known as a pneumothorax. Bleeding associated with lung biopsy is usually minor and can easily be controlled. Pneumothorax is sometimes required to be drained by either passing in a small needle or putting in a tube inside the pleural cavity, which can later be removed.
In case the child is having a complex lung condition or is suspected to have an interstitial lung disease or diffuse lung disease, you need to get in touch with a pediatric pulmonologist for a proper evaluation, consideration of lung biopsy and further treatment.