Bronchiolitis is a common respiratory infection in children under two years of age caused by viruses like respiratory syncytial virus, rhinovirus, adenovirus, metapneumovirus etc. This is a self-limiting infection and children usually improve in 7-10 days. Bronchiolitis obliterans is often confused with bronchiolitis but is a different condition.
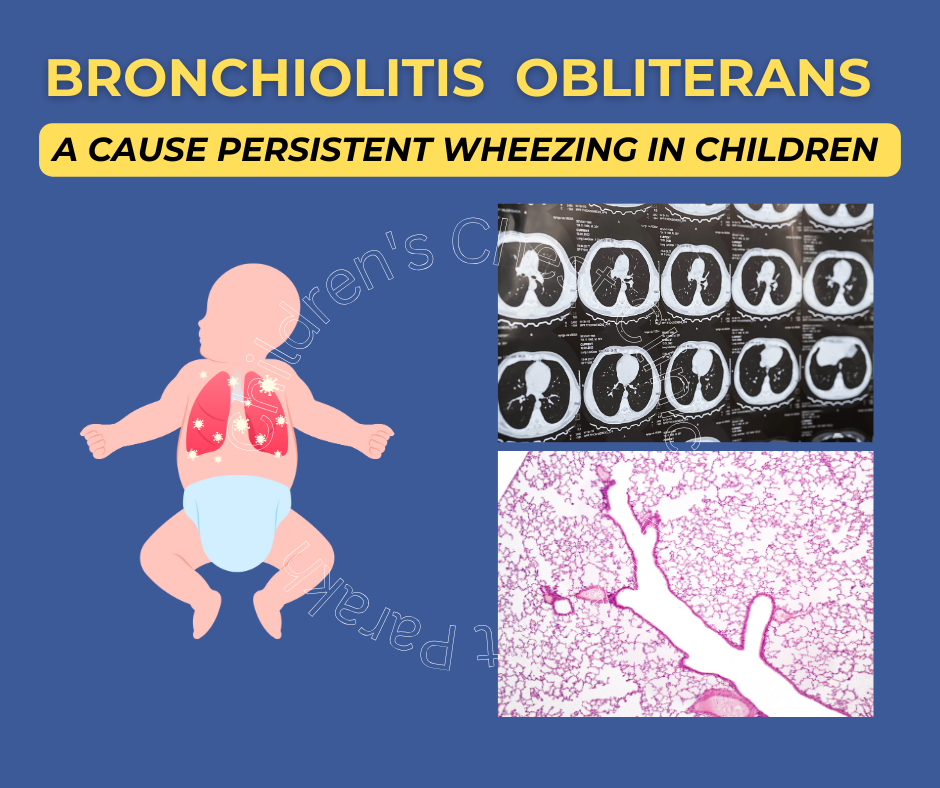
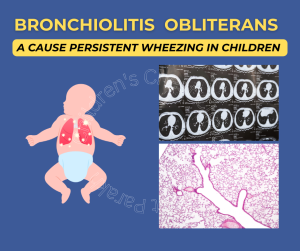
Bronchiolitis means inflammation in the small airways also known as bronchioles and obliterans means permanent narrowing. Bronchiolitis obliterans (BO) is a rare respiratory disease in children that leads to inflammation in the small airways (bronchioles), which causes the airways to scar and results in permanent narrowing. Unlike bronchiolitis usually gets better by itself, bronchiolitis obliterans is a chronic condition leading to permanent issues.
What causes bronchiolitis obliterans in children?
The most common cause of bronchiolitis obliterans in children in developing countries is respiratory viral infections. This condition is called post infectious bronchiolitis obliterans or PIBO. Many viruses are known to cause bronchiolitis obliterans, the most common being adenovirus. Other viruses which can lead to bronchiolitis obliterans are respiratory syncytial virus, rhinovirus etc. Other common causes of bronchiolitis obliterans seen in children are post bone marrow transplant and post lung transplant. Few autoimmune disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus or inflammatory bowel disease can lead to bronchiolitis obliterans. Rarely toxic chemical injury to the lungs can also lead to such problems.
What are the symptoms of bronchiolitis obliterans?
Children with bronchiolitis usually present with symptoms such as coughing, wheezing and fast breathing. These symptoms usually would settle down in a few days as mentioned. In some children, these symptoms persist for a longer period of time. Persistent symptoms of cough, wheezing, and fast breathing are the most common symptoms of post-infectious bronchiolitis obliterans. Symptoms of bronchiolitis obliterans could be variable from being mild in some children, but could be severe in many. Children with severe disease have significant problems breathing with need of oxygen and in some cases requirement of respiratory support. Frequent hospitalizations might be required in children with bronchiolitis obliterans.
How is bronchiolitis obliterans diagnosed?
The diagnosis of bronchiolitis obliterans is usually made based on the clinical features and radiological findings. The most important investigation for diagnosis is a CT scan of the chest. Children with bronchiolitis obliterans have a mosaic attenuation seen on CT scan. Other findings could be the presence of pneumonia and collapsed lung segments. In older children, we can also perform pulmonary function tests. In children with bronchiolitis obliterans there is severe obstruction which does not improve after giving bronchodilator medicine. In rare situations where the diagnosis is unclear we resort to a lung biopsy for the diagnosis.
How is bronchiolitis obliterans treated?
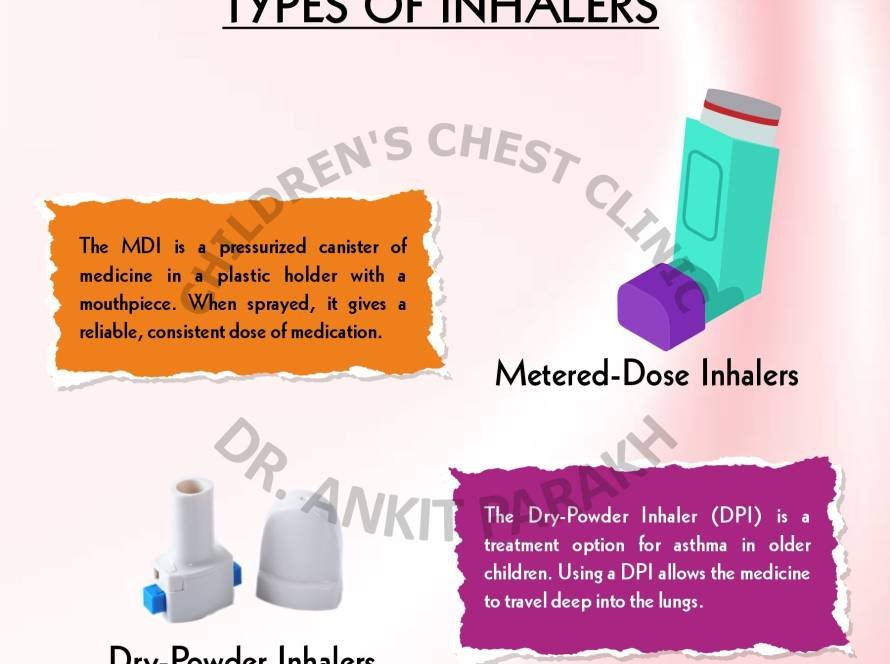
Early treatment of bronchiolitis obliterans is quite important As during the initial phase there is inflammation but later fibrosis sets in, leading to a permanent damage. Steroids are the most commonly used treatment. Higher than normal doses of steroids are used usually in the form of injection for 3 consecutive days. These injections are then used every month for a period of approximately 6 to 12 months. In addition, treatment such as azithromycin and inhaled corticosteroids are also used. Some children with a very severe disease which does not respond to steroids are candidates for a lung transplant.
In case your child is suffering from cough, wheezing or fast breathing which does not seem to be getting better you need to get in touch with the child chest specialist for guidance on further management.