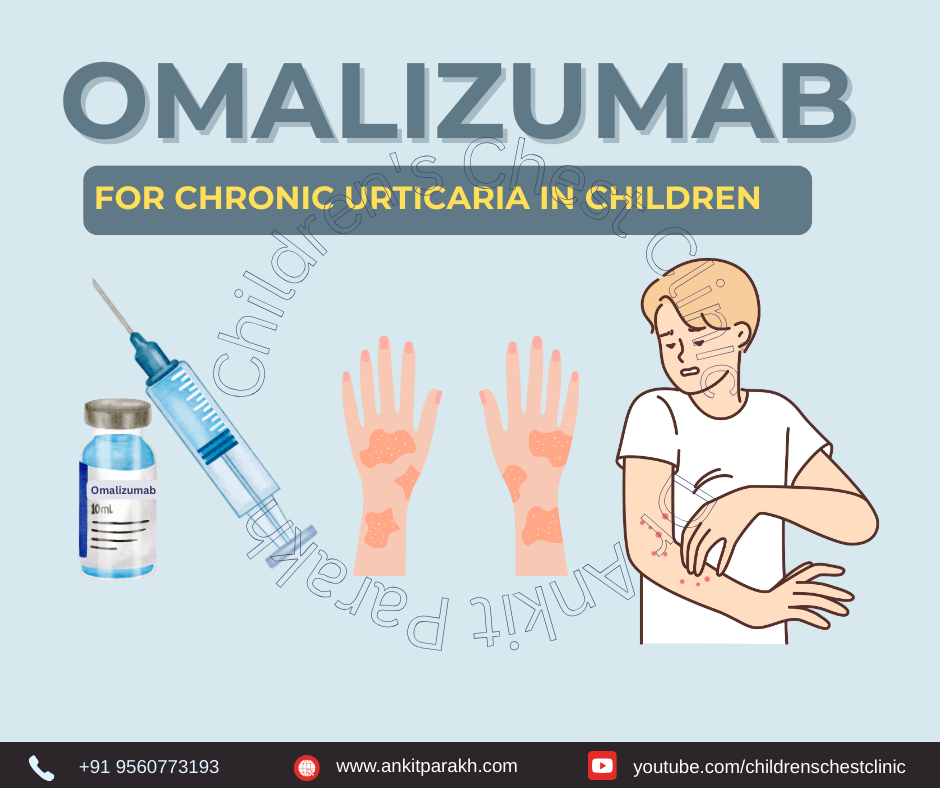
Chronic urticaria in children can be distressing for both patients and their families. Characterized by recurrent itchy hives and sometimes angioedema (swelling), it often disrupts sleep, school, and quality of life. When conventional antihistamines fail, Omalizumab—a monoclonal antibody—offers a promising and effective treatment option. This article provides an overview of how Omalizumab works and its role in managing chronic urticaria in children.
What is Chronic Urticaria?
Chronic urticaria is defined as the presence of hives, with or without angioedema, lasting for more than six weeks. It can be:
Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU): Occurs without a clear trigger.
Chronic inducible urticaria: Triggered by physical factors like cold, heat, or pressure.
In many cases, the exact cause is unknown, making long-term management challenging.
Challenges in Treating Chronic Urticaria
First-line treatment for chronic urticaria includes second-generation non-sedating antihistamines. Some children may require higher doses, but a significant number still experience persistent symptoms despite these measures. This is where Omalizumab becomes a valuable option.
What is Omalizumab?
Omalizumab is a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody that targets IgE, a key player in allergic responses. By binding to IgE, Omalizumab prevents it from interacting with immune cells, thereby reducing the release of histamine and other chemicals responsible for hives and swelling.
Originally developed for asthma, Omalizumab has been approved for the treatment of chronic spontaneous urticaria in children aged 12 years and older who do not respond to antihistamines.
How is Omalizumab Administered?
Given as a subcutaneous injection (under the skin)
Administered once every 4 weeks
Dosage is based on body weight and IgE levels in asthma, but for urticaria, a standard dose (usually 150 mg or 300 mg) is used regardless of IgE levels
The treatment is usually initiated and monitored by a pediatric allergy specialist.
Effectiveness of Omalizumab in Children
Clinical studies and real-world evidence have shown:
Rapid improvement in hives and itching, often within a few weeks
Reduced need for antihistamines or corticosteroids
Improved sleep and quality of life
Minimal side effects in most children
It is important to continue regular follow-up to assess response and decide on the duration of therapy.
Is Omalizumab Safe for Children?
Yes, Omalizumab is generally well-tolerated. Common side effects include:
Mild injection site reactions (redness, swelling)
Headache
Rarely, allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), so the first few doses are typically given in a clinical setting with observation
Long-term safety data in children is encouraging but still being monitored.
Managing chronic urticaria in children can be complex, especially when standard treatments fail. Omalizumab offers a safe and effective alternative that can significantly improve quality of life for affected children. As with all biologic therapies, its use should be guided by a pediatric allergy specialist to ensure appropriate monitoring and maximum benefit.
Conclusion
1. When should Omalizumab be considered in chronic urticaria?
Omalizumab is recommended when symptoms persist despite high-dose antihistamines and impact the child’s daily life or sleep.
2. How soon does Omalizumab work for chronic urticaria?
Many children show improvement within 1–4 weeks, although full response may take up to 12 weeks.
3. Can Omalizumab be stopped once symptoms improve?
Yes, after several months of successful treatment, your doctor may consider tapering or stopping therapy while monitoring for recurrence.
4. Is Omalizumab approved for all children with urticaria?
Currently, it is approved for children 12 years and older with chronic spontaneous urticaria unresponsive to antihistamines.
5. Does Omalizumab cure chronic urticaria?
Omalizumab controls symptoms but does not cure the condition. Many children experience remission over time, and treatment may eventually be discontinued.