Cystic Fibrosis-Related Liver Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Cystic Fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder that primarily affects the lungs and digestive system, but it can also lead to liver complications. Cystic Fibrosis-Related Liver Disease (CFLD) occurs due to thick mucus obstructing the bile ducts, leading to liver damage over time. Early detection and management are crucial in preventing severe complications such as cirrhosis and liver failure.
How Does Cystic Fibrosis Affect the Liver?
The liver produces bile, which aids in digesting fats. In children with Cystic Fibrosis (CF) , the thick mucus clogs the bile ducts, leading to bile stasis, inflammation, and scarring (fibrosis). Over time, this can progress to more severe liver conditions, including cirrhosis.
Common Liver Problems in Children with Cystic Fibrosis
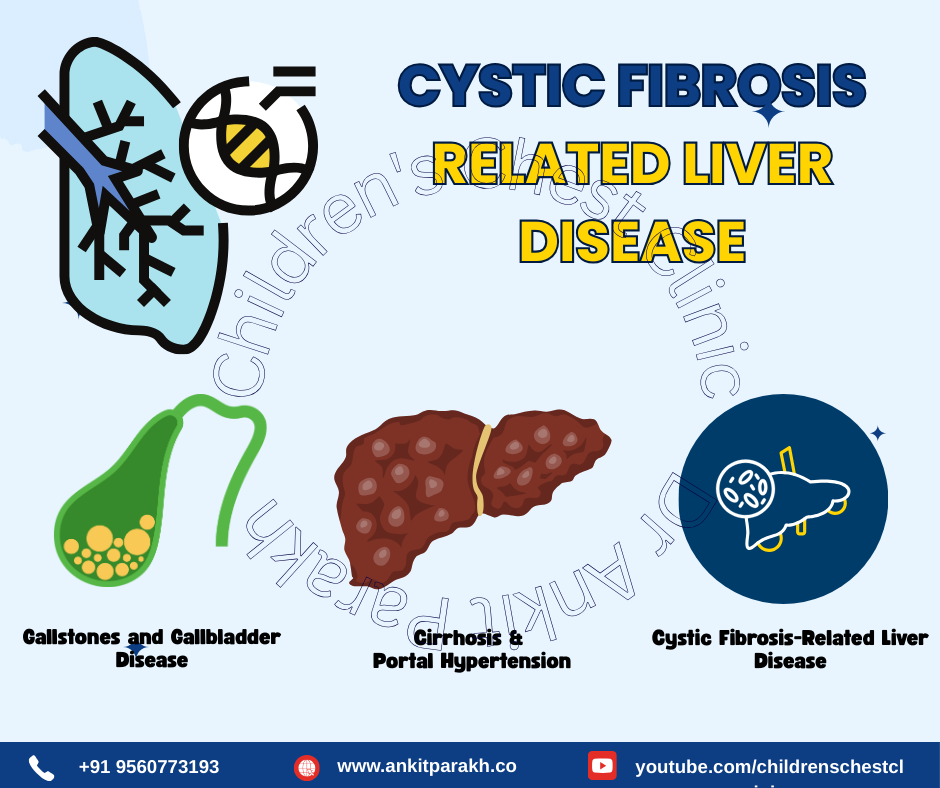
1. Cystic Fibrosis-Related Liver Disease (CFLD)
Cystic Fibrosis-Related Liver Disease (CFLD) is characterized by bile duct obstruction, inflammation, and liver fibrosis. Symptoms include enlarged liver (hepatomegaly), abnormal liver enzyme levels, jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes), fatigue and poor growth. Management includes regular liver function monitoring, ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) therapy to improve bile flow, and nutritional support.
2. Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension
Advanced Cystic Fibrosis-Related Liver Disease (CFLD) can lead to cirrhosis, a condition where the liver becomes scarred and loses its function. Portal hypertension occurs due to increased blood pressure in the portal vein, causing an enlarged spleen (splenomegaly), ascites (fluid buildup in the abdomen) and increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding. Management includes medications to manage complications, nutritional support, and in severe cases, liver transplantation.
3. Gallstones and Gallbladder Disease
Children with CF have a higher risk of developing gallstones due to poor bile flow and altered fat metabolism. Gallstones can cause abdominal pain (especially after fatty meals), nausea and vomiting and jaundice in severe cases. Management includes dietary modifications, UDCA therapy, and in severe cases, gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy).
Diagnosis and Monitoring
Early detection of Cystic Fibrosis-Related Liver Disease (CFLD) is crucial. Tests include Liver function tests (LFTs) to check enzyme levels, abdominal ultrasound to assess liver and gallbladder health and FibroScan and liver biopsy in severe cases.
Treatment and Prevention
Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCA): Helps improve bile flow and reduce liver damage.
Nutritional Support: High-calorie, high-protein diet with vitamin supplements (especially fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K).
Regular Monitoring: Liver function tests and imaging help track disease progression.
Managing CF Effectively: Ensuring good lung health and preventing infections can indirectly support liver function.
Cystic Fibrosis-Related Liver Disease is a significant concern in children with Cystic Fibrosis (CF) . Early detection, proper management with UDCA, nutritional support, and regular monitoring can help prevent severe complications. A multidisciplinary approach involving pediatric pulmonologists, gastroenterologists, and dietitians is essential for optimal care.
Conclusion
1. What is Cystic Fibrosis-Related Liver Disease (CFLD)?
Cystic Fibrosis-Related Liver Disease (CFLD) occurs when thick mucus blocks bile ducts, leading to liver inflammation, fibrosis, and potential liver damage.
2. How common is liver disease in children with Cystic Fibrosis?
Approximately 5-10% of children with Cystic Fibrosis (CF) develop significant liver disease, but many may have mild liver involvement.
3. What are the symptoms of gallstones in children with Cystic Fibrosis (CF) ?
Symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and jaundice in severe cases.
4. How is Cystic Fibrosis-Related Liver Disease (CFLD) diagnosed?
Liver function tests, ultrasound, and sometimes a liver biopsy or FibroScan are used to diagnose Cystic Fibrosis-Related Liver Disease (CFLD) .
5. Can liver disease in Cystic Fibrosis (CF) be prevented?
While it cannot always be prevented, early detection, UDCA therapy, good nutrition, and regular monitoring can help manage the condition effectively.