Bones of the face around the nose have hollow air spaces which are called sinuses. There are four sets of sinuses located in the cheekbones (maxillary sinuses), forehead (frontal sinuses), between the eyes (ethmoidal sinuses) and behind the eyes and nasal passages (sphenoid sinuses). Sinuses share the same lining or the mucous membrane as the nose and mouth.
What causes sinusitis in children?
Young children are more predisposed to have upper respiratory infections, most of which are viral. Since the lining of the nose and sinuses are common, viral infections cause swelling of the mucosa of the sinuses. Increased mucus inside the sinuses and swollen lining blocks the sinuses, providing a good environment for bacteria to grow. This leads to a sinus infection or sinusitis. The most common bacteria that cause acute sinusitis are streptococcus pneumonia, haemophilus influenzae and moraxella catarrhalis. Allergy also predisposes a child to sinusitis as children with allergy also get swollen mucosa of the sinuses.

What are the symptoms of sinusitis in children?
The symptoms of sinusitis in children could be a persistent cold lasting for more than 10-14 days, thick yellow-green nasal discharge and a post nasal drip. Children sometimes can get fever, sore throat and a bad breath. Older children can also complain of a headache. Sometimes swelling can be seen around the eyes.
Sinusitis could be acute or chronic. Chronic sinusitis lasts 12 weeks or longer, and the usual causes are allergy and prolonged inflammation, instead of an infection.
What are the other conditions which present with chronic sinusitis?
In children with chronic sinusitis certain systemic diseases should be considered. These conditions are cystic fibrosis, primary ciliary dyskinesia, allergic fungal sinusitis, immunodeficiency and wegener’s granulomatosis. Certain structural problems like deviated nasal septum and enlarged adenoids also predispose to sinusitis.
How are children with sinusitis managed?
A detailed medical history and examination usually is sufficient to make a diagnosis of sinusitis. In some children Xray of sinuses or CT Scan might be needed especially when complications of sinuses are suspected. Occasionally, we might need to do a nasal endoscopy for a detailed examination of the nose.
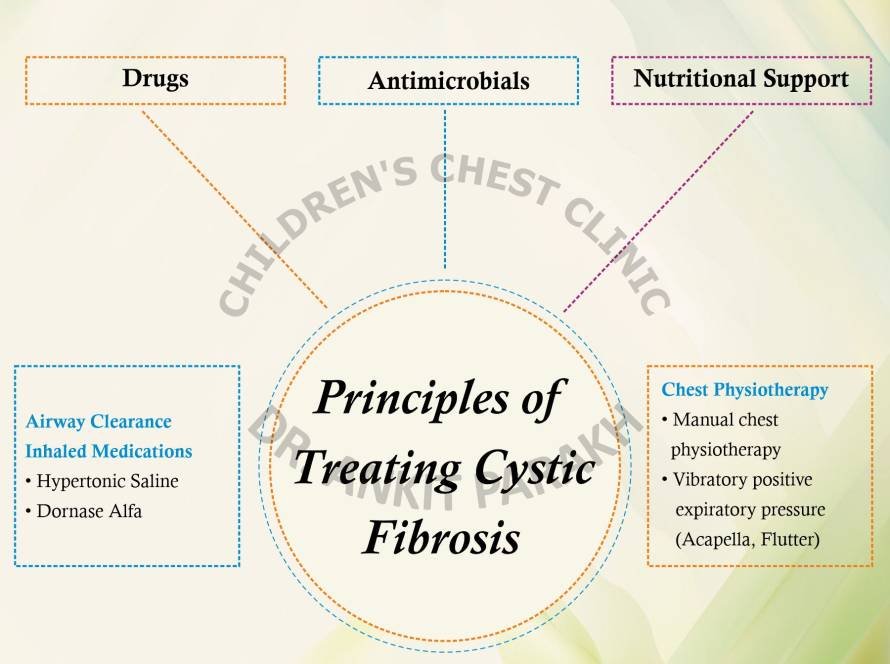
Children with acute sinusitis require 7-10 days of antibiotics. Nasal steroid sprays and nasal saline (saltwater) gentle sprays might be needed for a short-term relief of symptoms. Children with chronic sinusitis require long-term antibiotics and steroid sprays. Some older children who are unresponsive to treatment might require surgical treatment like removing adenoids or widening the opening of the sinuses.
What could be the complications of sinusitis in children?
Sinus infection can spread to the nearby areas and lead to complications. The most common complication (accounting for 80% of all complications) of sinusitis is involvement of the orbit (eye socket) leading to infection of the orbital space called orbital cellulitis. Occasionally the infection can travel into the brain leading to pus collection causing abscesses, meningitis and dural sinus thrombophlebitis.
If your child is having symptoms of sinusitis you need to get in touch with a pediatric pulmonologist for proper diagnosis and treatment.