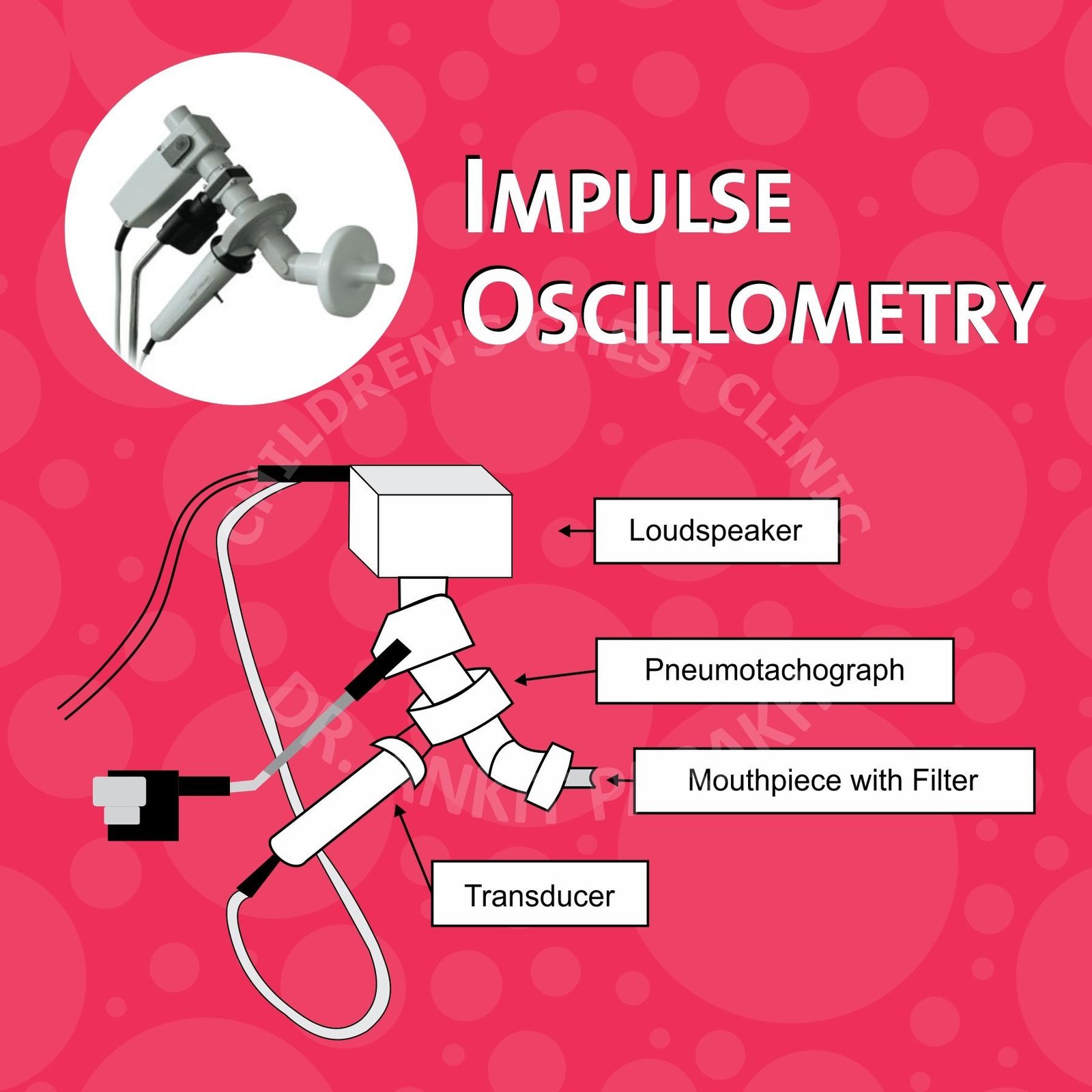
Impulse Oscillometry
What is Impulse Oscillometry?
Impulse Oscillometry is a technique that measures airway resistance and reactance during normal breathing. Unlike spirometry, it does not require forceful breathing efforts, making it ideal for young children and those unable to perform complex maneuvers. By delivering sound waves through a mouthpiece, IOS analyzes how the waves interact with the respiratory system, providing detailed insights into airway mechanics.
Importance of Impulse Oscillometry in Children
IOS offers several advantages in pediatric care:
- Ease of Use: Requires minimal cooperation, making it suitable for children as young as three years old.
- Detailed Airway Analysis: Provides comprehensive data on large and small airway function.
- Early Detection: Identifies early airway changes in conditions like asthma before significant symptoms appear.
- Non-Invasive and Safe: The procedure is comfortable and poses no risk to the child.
Key Applications of Impulse Oscillometry
- Diagnoses and monitors asthma by assessing airway resistance and reactance.
- Evaluates bronchodilator responsiveness to guide treatment.
- Identifies underlying airway abnormalities contributing to persistent cough.
- Detects and helps in follow up of conditions like cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis and restrictive lung diseases.
How is Impulse Oscillometry Performed?
The procedure for IOS is simple and child-friendly:
- Preparation: The child is seated comfortably and instructed to breathe normally through a mouthpiece connected to the IOS device. Each reading is for 20 second or so and usually takes 3-5 readings are taken.
- Measurement: Sound waves are generated by the device and travel through the airways. The child’s response to these waves is recorded by a computerized sensor. Results are then calculated by the software and presented as graphs and values.
- Duration: The test typically takes 5-10 minutes and may be repeated to ensure accuracy.
- Analysis: Results are compared with age-appropriate reference values to assess airway function.
Benefits of Impulse Oscillometry in Pediatric Care
- Provides objective measurements of airway function without requiring complex breathing efforts.
- Facilitates early diagnosis and tailored management of respiratory conditions.
- Offers a reliable alternative to spirometry for young children or those with physical or cognitive challenges.
Impulse Oscillometry (IOS) is a game-changer in pediatric respiratory care, offering a reliable, non-invasive method to assess lung function in young children and those with respiratory challenges. As a type of Pulmonary Function Test (PFT), it provides critical insights into conditions like Asthma in Young Children and chronic cough, enabling early diagnosis and effective management.
Conclusion
Impulse Oscillometry services at BLK MAX and Children’s Chest Clinic
Children’s Chest Clinic and Division of Pediatric Pulmonology at BLK-MAX Hospital we have a state of the art Impulse Oscillometry equipment, MS-IOS from Jeager (Germany). The equipment can also perform a spirometry. We also specially trained child friendly technicians would help the child perform the test. Dr Ankit Parakh himself takes special interest in getting these tests done.
Pediatric Lung Function Testing
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What makes Impulse Oscillometry suitable for young children?
IOS requires only normal breathing and minimal cooperation, making it ideal for children as young as three years old.
2. Can Impulse Oscillometry diagnose asthma?
Yes, IOS can detect airway resistance and changes associated with asthma, helping in diagnosis and treatment monitoring.
3. Is Impulse Oscillometry safe for children?
Yes, IOS is a non-invasive and safe procedure with no discomfort or risks.
4. How does IOS differ from spirometry?
Unlike spirometry, IOS does not require forceful breathing, making it easier for young children or those unable to perform complex maneuvers.
5. What conditions can IOS help identify?
IOS is most useful for evaluation of children with chronic cough, wheezing and suspected asthma. It can also be helpful in management of other childhood respiratory problems like cytic fibrosis, bronchiectasis and restrictive lung diseases.



